350 KVA 400V to 140V Al wire 3PH isolation transformer
Cat:Three Phase transformer
Three-phase isolation transformer series products are widely used in industrial and mining enterprises, power plants, airports, high-rise buildings, s...
See DetailsWhat is the cause of overcurrent in the compressor?
If the so-called overcurrent refers to the input current overcurrent of a transformer, there may be the following reasons:
1. Transformer saturation. As is well known, transformer windings exhibit inductance under alternating current, with a high AC impedance that is proportional to the magnetic permeability. At the same time, magnetic materials all have a saturation magnetic flux density. If the transformer is not designed properly or biased, the working magnetic flux density of the transformer will be too high. When it is greater than the saturation magnetic flux density, the magnetic permeability will drop to 0. At this time, the AC impedance of the transformer is only the resistance impedance, which is equivalent to directly connecting the positive and negative poles of the power supply to a wire. The consequences can be imagined. In switch mode power supplies, this phenomenon often occurs in push-pull topologies, where capacitors are connected in series on the primary side to solve the problem of magnetic bias.
2. Load short circuit!!
3. The insulation of the transformer winding is not well done, resulting in inter-turn short circuits or short circuits in the primary and secondary windings.
4. Some characteristic issues with magnetic core materials, such as not considering the effects of DC bias and temperature on magnetic permeability during design, can to a decrease in transformer winding impedance and overcurrent under high temperature and high DC bias.
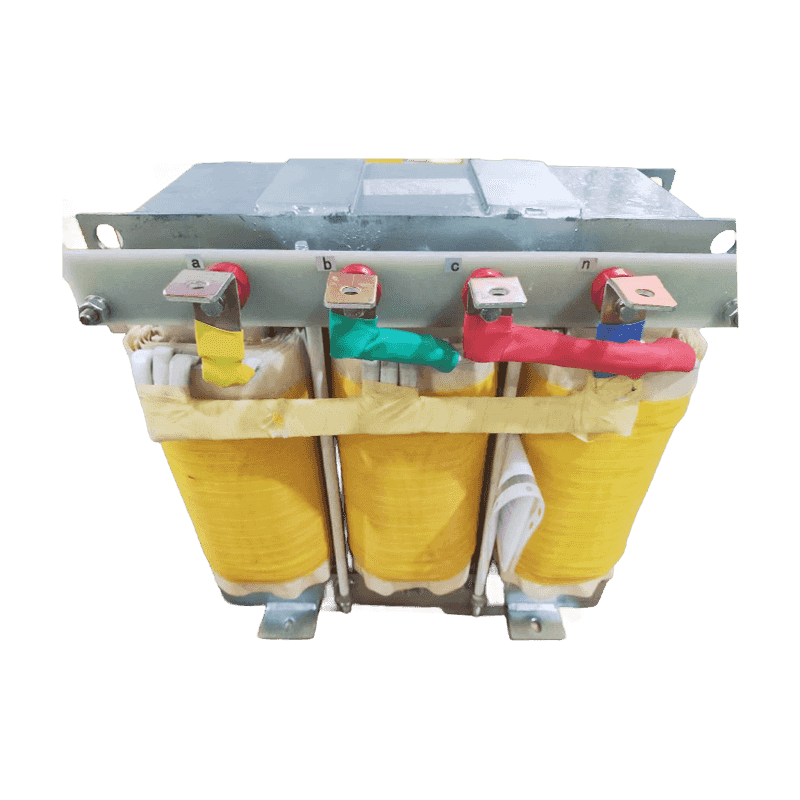
Three-phase isolation transformer series products are widely used in industrial and mining enterprises, power plants, airports, high-rise buildings, s...
See Details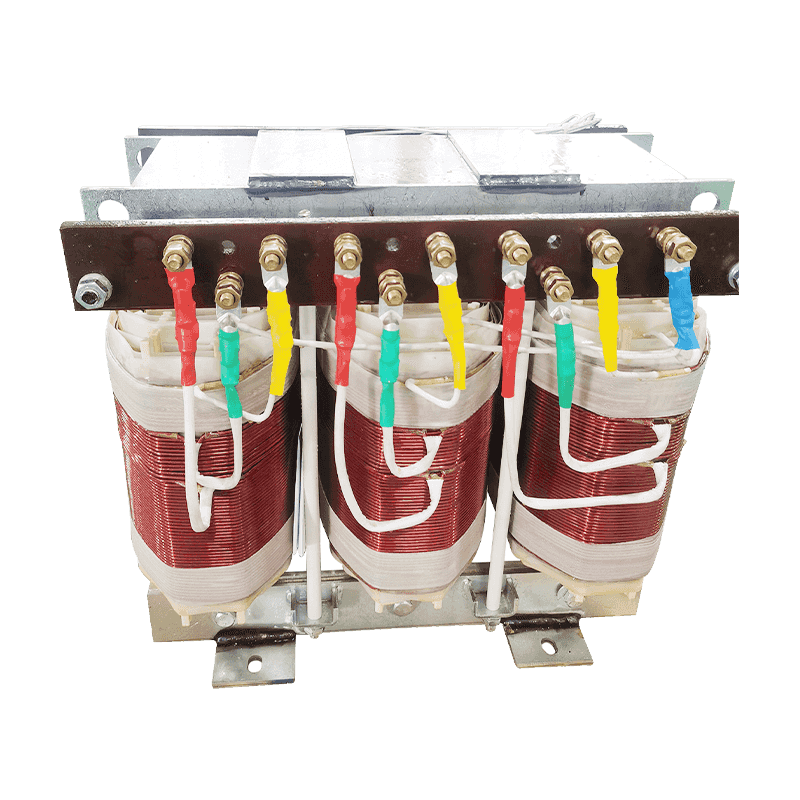
An autotransformer is a special transformer in which the output and input share a common set of coils. Step-up and step-down are realized with differe...
See Details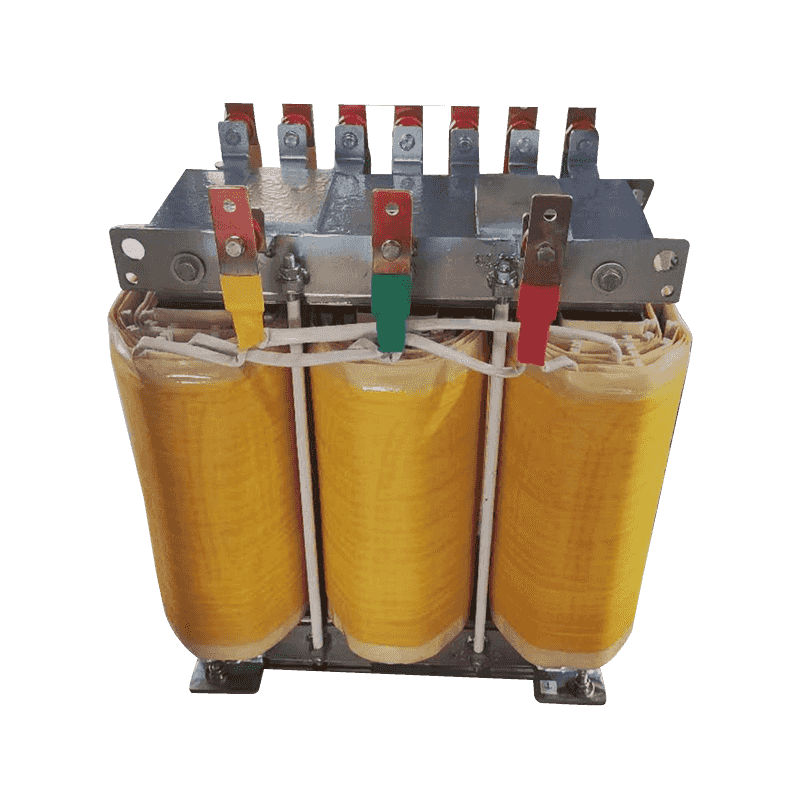
A three-phase step-up transformer is an electrical device used to convert low-voltage three-phase alternating current to high-voltage three-phase alte...
See Details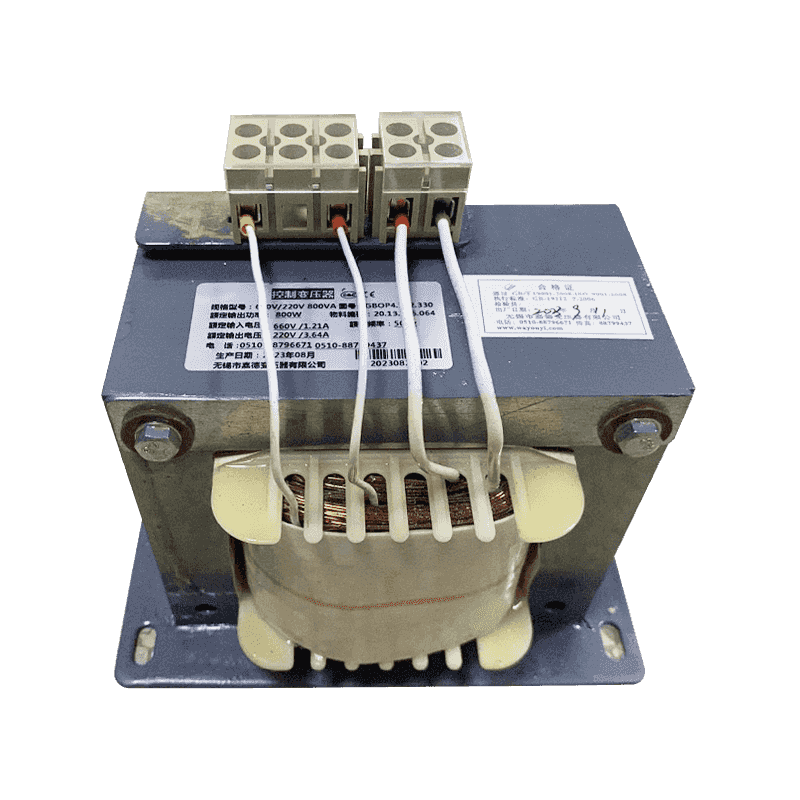
A control transformer is an electrical device used to control the magnitude of AC voltage. It consists of a primary winding and a secondary winding, w...
See Details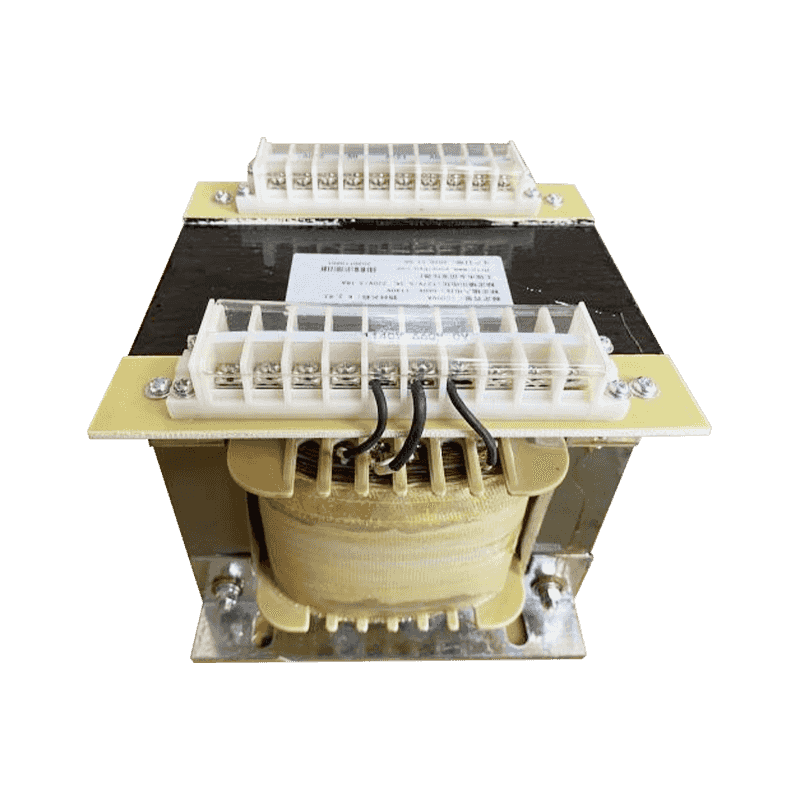
The 1500 VA power control transformer is mainly used to control and regulate the power supply of other circuits or devices, ensuring the stability and...
See Details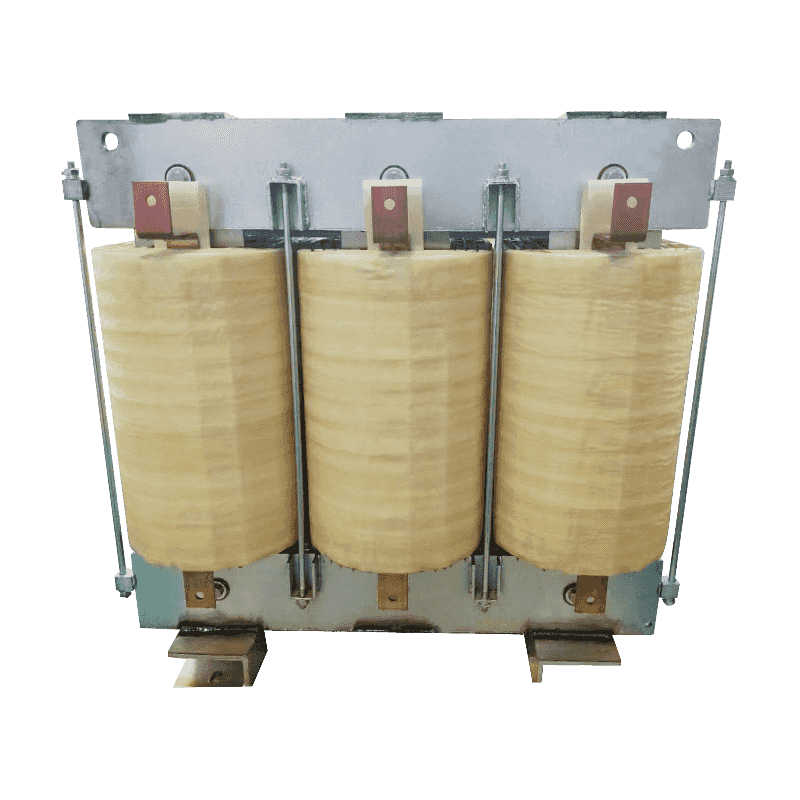
Product Features:A three-phase loading reactor is a device used to regulate and control the power factor within electrical power systems. It typically...
See Details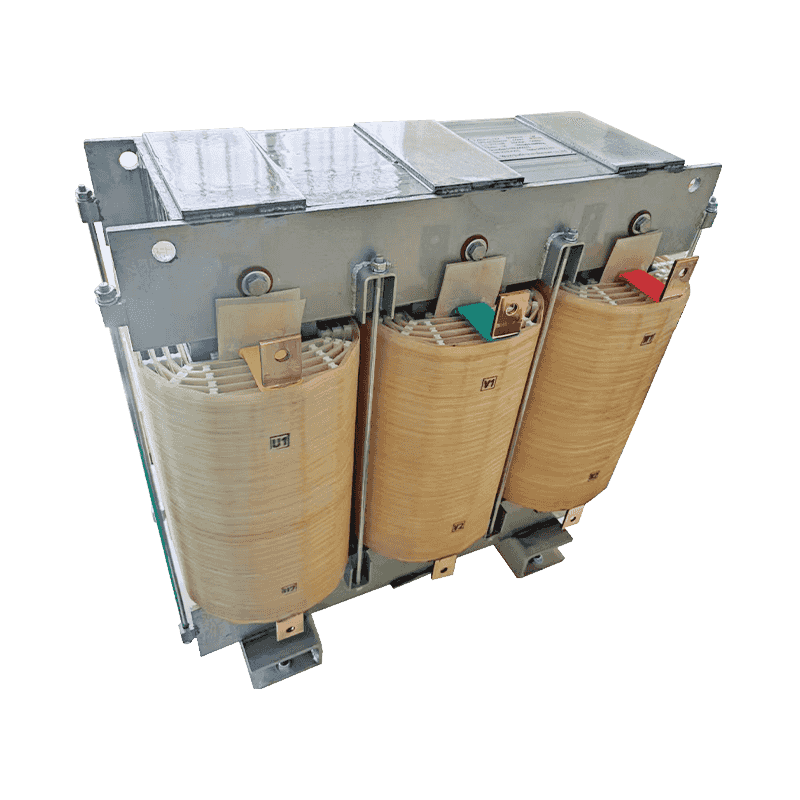
Product Features: A three-phase loading reactor, as an indispensable device in power systems, primarily functions to regulate and optimize the power f...
See Details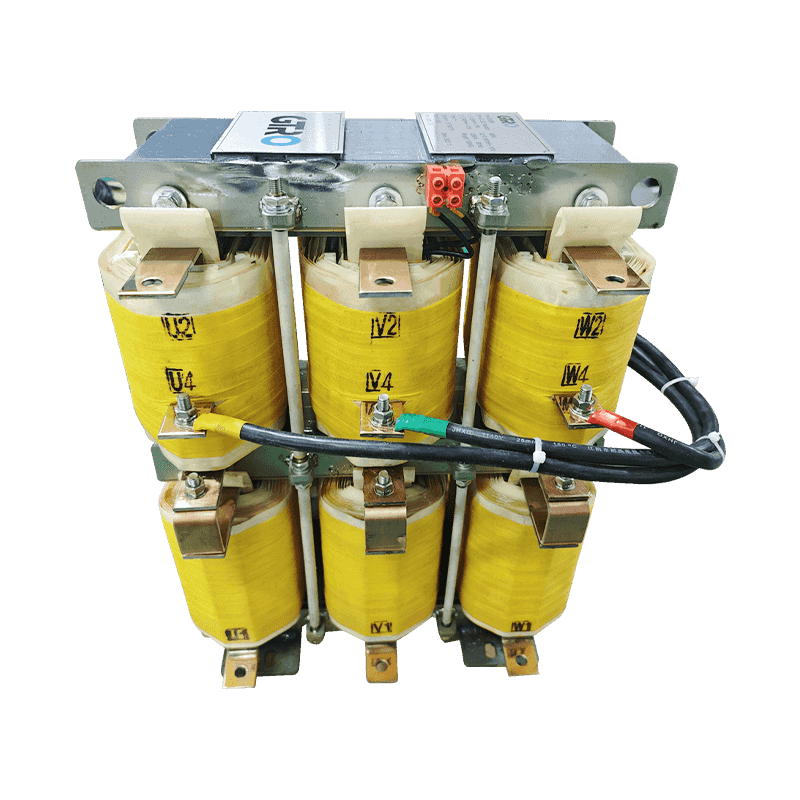
Product FeaturesLCL filter reactor is a common power supply filter reactor, mainly used in DC power supply three-phase converter filtering at the outp...
See Details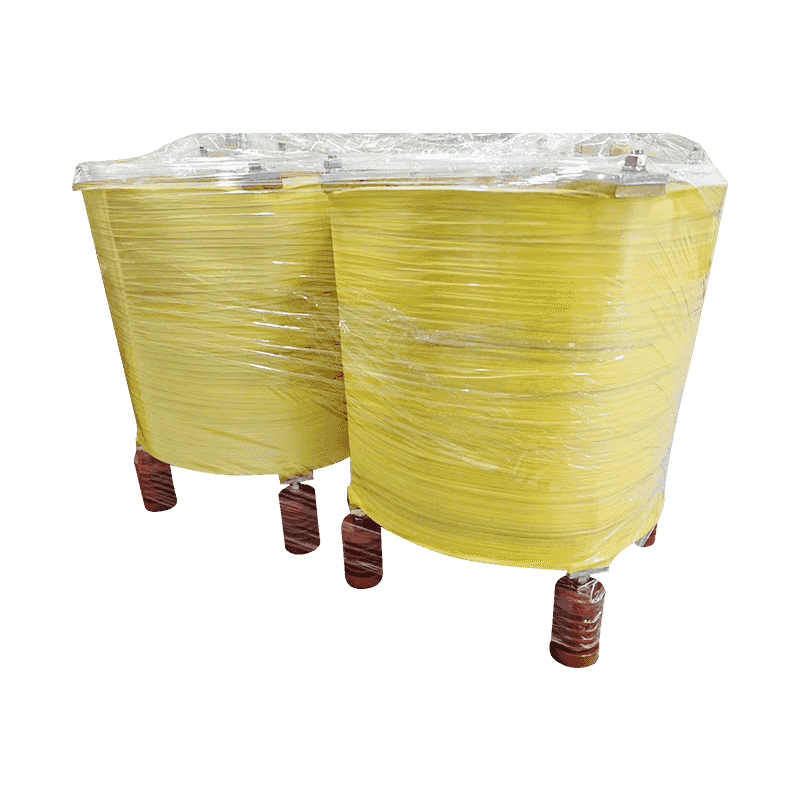
Air core reactors are primarily used in power systems for limiting short-circuit currents, reactive power compensation, and phase-shifting. Magnetic f...
See Details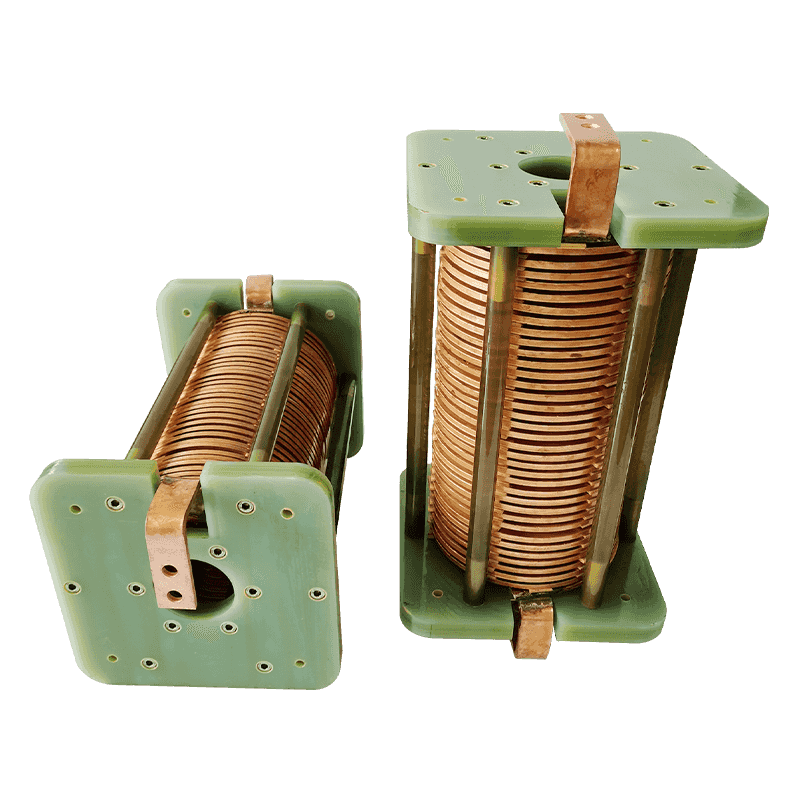
In power systems, the Air Core Reactor serves as a critical high-voltage device, fulfilling essential functions such as limiting short-circuit current...
See DetailsCopyright © 2024. Wuxi Jiade Transformer Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Wholesale Magnetoelectric Devices Suppliers

Contact Us