20 KVA Epoxy resin Three Phase Dry type transformer
Cat:Three Phase transformer
Epoxy resin three-phase dry-type transformerFeatures:1. Improve insulation strength and electrical resistanceEpoxy resin is a great electrical insulat...
See Details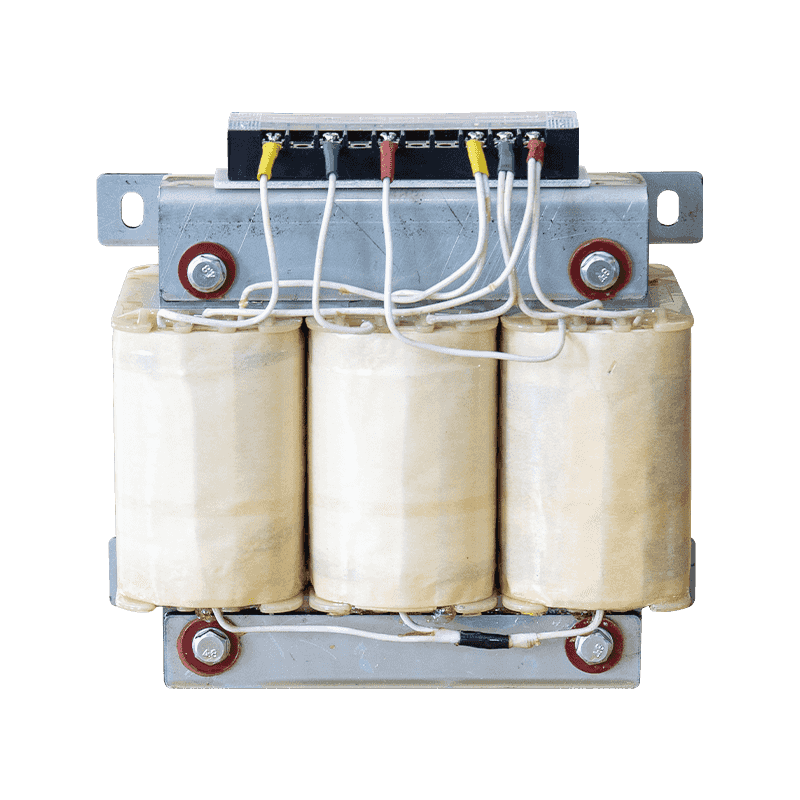
The three-phase step-down transformer is a fundamental component in electrical power distribution, widely used to reduce voltage levels for industrial, commercial, and residential applications. However, a common question arises: Can a three-phase step-down transformer be used in reverse for step-up applications? The short answer is yes, but with important limitations and considerations.
A three-phase step-down transformer is designed to convert high primary voltage to a lower secondary voltage, typically to match the requirements of end-use equipment. Its operation relies on electromagnetic induction, where alternating current in the primary winding generates a magnetic field, inducing a proportional voltage in the secondary winding.
The turns ratio (primary to secondary winding turns) determines the voltage transformation. For example, a transformer with a 10:1 turns ratio will reduce voltage by a factor of 10. Reversing the transformer means applying power to the secondary winding, effectively turning it into a step-up transformer.
While theoretically possible, several critical factors must be evaluated before repurposing a three-phase step-down transformer for step-up operation:
The original design parameters of the transformer must be respected. If the secondary winding (now acting as the primary) was not designed to handle the higher input current, overheating and insulation failure may occur. Exceeding rated current can lead to catastrophic failure.
Transformers are optimized for their intended direction of power flow. When reversed, impedance mismatches may cause inefficient operation, increased losses, and potential voltage instability.
The transformer core is designed for a specific flux density. If the reversed operation leads to excessive flux, core saturation can occur, resulting in distorted waveforms, overheating, and potential damage.
The insulation system in a step-down transformer is rated for the original voltage distribution. If the low-voltage winding is subjected to higher voltages in reverse operation, insulation breakdown becomes a risk.
Most three-phase step-down transformers have built-in protection mechanisms (e.g., overcurrent relays) calibrated for standard operation. Reversing the transformer may require additional protective measures to prevent faults.
In certain scenarios, using a three-phase step-down transformer in reverse is feasible, provided the operational limits are strictly observed:
However, permanent or high-power applications should avoid this practice unless the transformer is explicitly rated for bidirectional operation.
Electrical codes and standards (e.g., IEEE, IEC) typically do not endorse using transformers outside their specified ratings. Reversing a three-phase step-down transformer may void certifications and pose legal liabilities in case of accidents.
While a three-phase step-down transformer can technically function as a step-up transformer when reversed, doing so introduces significant risks. Voltage mismatches, insulation stress, core saturation, and efficiency losses are major concerns that must be carefully managed. For critical applications, using a purpose-built step-up transformer is always the safer and more reliable choice.
For engineers considering reverse operation, a thorough risk assessment and controlled testing are essential to prevent equipment damage and ensure operational safety.
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Feasibility | Possible in theory | High risk of failure if not properly managed |
| Cost | Avoids purchasing a new step-up transformer | Potential damage may lead to higher costs |
| Efficiency | May work in low-power scenarios | Increased losses and reduced efficiency |
| Safety | Can be used in emergencies | Violates safety standards if unapproved |
| Longevity | Short-term use may be acceptable | Accelerated wear and insulation degradation |
This structured approach ensures clarity while maintaining technical accuracy and readability. Let me know if you’d like any refinements!
Contact Us